- No products in the cart.
Description
Composition
Dosage
Safety Information
Additional Information
Description
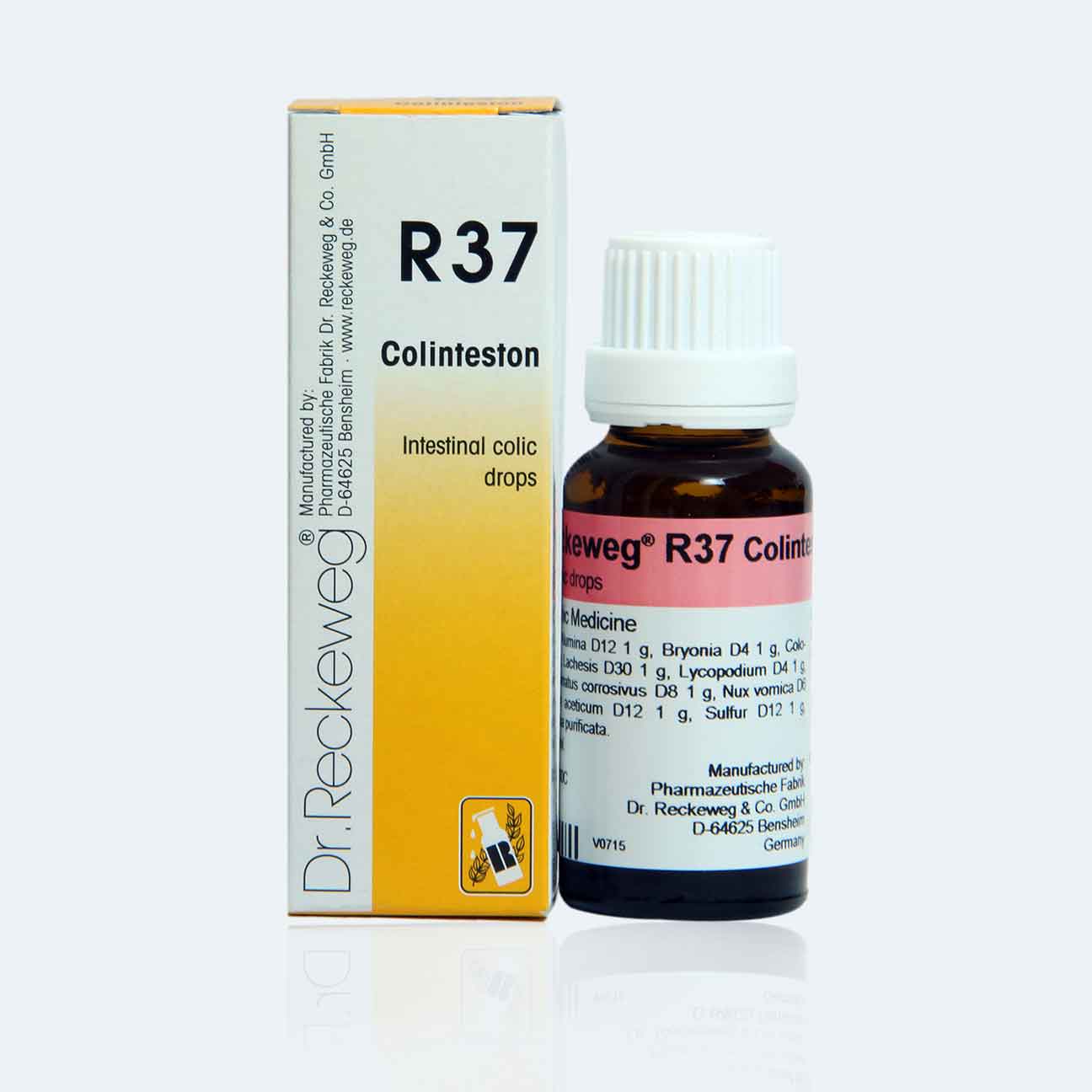
Information about Dr. Reckeweg R37 Intestinal Colic Drops
Dr. Reckeweg R37 Intestinal Colic Drops is a homeopathic medicine commonly indicated to treat for Intestinal colic which is cramp-like pain that originates in the small or large intestine due to bloackage.
Size: 22 ml
Product Origin: Germany
Key Benefits:
- It helps to cure Flatulent colic, meteorism, porphyrinuria, intestinal colic, abdominal spasms of varying genesis which are characteristic in porphyrinuria and affected liver.
- it is cure the Cirrhosis of the liver, bilious colic; colic in saturnism, dysmenorrhoea; Complementary remedy for renal colic.
- In case of chronic constipation gradual regularizing effect.
Composition
Composition
- Alumina
- Bryonia
- Colocynthis
- Lachesis
- Lycopodium
- Mercur. subl. corros.
- Nux vomica.
- Plumbum acet.
- Sulfur
Dosage
Dosage
Directions for use:
- As prolonged cure 3 times daily 10-15 drops in a little water before meals.
- In case of intermittent pains, colic, meteorism and suspected perforation, (eventually the undiluted drops can be held in the mouth and spad out), take for a short while, 1/2-1 hour every 3-5 minutes 5-10-15 drops.
- In case of fundamental changes, bilious colic, renal colic, inflammation of the appendix and others, the following remarks apply
Safety Information
Safety Information
- Read the label carefully before use.
- Store in a cool and dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Keep out of reach of children
Additional Information
Additional Information
Ingredients: Alumina D12, Bryonia D 4, Colocynthis D 4, Lachesis D 30, Lycopodium D 4, Mercur subl. corr. D 8, Nux vomica D 6, Plumbum acetic. D12, Sulfur D12, Ethanol, Aqua pur.
Mode of action:
It is a fact that the liver governs almost the whole detoxicating system in the organism, especially in the intestines. All the food decomposed in the intestines is directed towards the liver, except for the fats which are concentrated in the chylifies. It follows that the functional disorders of the liver will involve a repercussion in the intestines (stoppages). On the other hand the liver sends toxic elements outwards through the intestines. In this connection cholesterics and porphyrins deserve special mention as intermediaries among the hemoglobin tissues; they are consumed by the liver. In modern therapy the liver is exposed to harmful reoxidation in many ways. This entails a merely intermittent emission or absorption of intermediary elements and this intermittence has repercussions in the intestines. The outcome is flatulence, meteorism, flatulent colic, intestinal cramps which are often considered as the after-effects of appendicitis or even of tumors. These ailments can also be induced by nicotine. Chronic constipation is a frequent concomitant and R 37 becomes even more imperative.
Alumina: Stool in small lumps; constipation.
Bryonia: Constipation; dark stools.
Colocynthis: Flatulent colic; tendency to contraction.
Lachesis: Bad digestion especially after an excess of quinine or alcohol.
Lycopodium: Flatulent in the evening.
Mercur. subl. corros.: Tenesmus, dysenteriform intestinal cramps.
Nux vomica: Intestinal spasms.
Plumbum acet.: Intestinal colic. Watery and nauseous stools; chronic
diarrhoea. Abdomen very sensitive to touch.
Sulfur: Reaction agent, malodorous flatulence, swelling of the abdomen.
Matutinal diarrhoea.
R 37 regularizes stools and will end constipation in many cases.
Remarks:
- In gallbladder colic: additionally or alternately with R 7.
- In kidney stone colic: additionally or alternately with R 27.
- To sedate: compare R 14.
- In enterocolitis: alternate with R 4.
- In duodenal ulcer and gastritis: additionally R 5.
- In pancreatitis: see R 72.